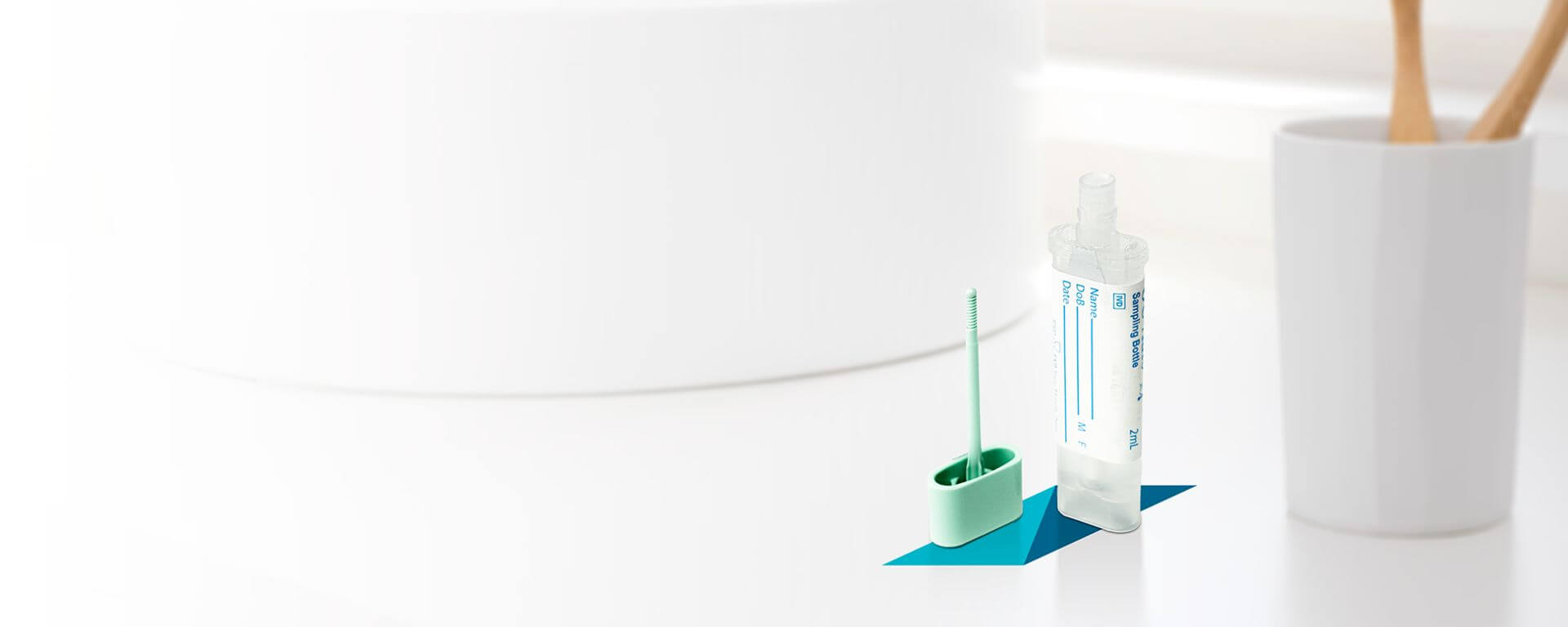

OC-AUTO® FIT
Improving colorectal cancer screening saves lives



Listen to Gladys’ heartfelt story about the life-saving power of OC-Auto FIT
When Gladys screened with OC-Auto FIT following an annual checkup, she never expected that it would lead to a diagnosis of colon cancer—the same cancer her late husband had suffered from. Watch the video to see why it’s crucial for average-risk* patients over 45 to get screened yearly with OC-Auto FIT.
Watch now

Colorectal cancer (CRC) has the second-highest death rate among cancers. If detected at an early stage, 90% of all CRC deaths are preventable, but over 30% of adults ages 50-75 are not getting screened as recommended.1,2
Tier 1 recommendations support annual FIT screening for 45–75 year olds3,4,5
To improve patient outcomes for average-risk adults, the US Preventive Services Task Force, American College of Gastroenterology, and the US Multi-Society Task Force on Colorectal Cancer

Annual FIT

Colonoscopy every 10 years
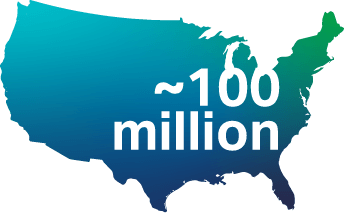
Based on the new guidelines, nearly 100 million US adults should be screened annually.

Advancing CRC screening is critical. Choosing a CRC screening solution is simple
The only Tier 1, guideline-recommended FIT backed by proven clinical outcomes3,6
- The #1 automated noninvasive CRC screening tool in the world7
- Excellent sensitivity and specificity
- Easier at-home screening for patients
- Customizable programmatic services to help optimize screening

“The OC-Light and the OC FIT-CHEK® family of FITs have the best test performance characteristics (ie, highest sensitivity and specificity).”8
–US Preventive Services Task Force

“The fecal immunochemical test product [by Polymedco] is the FIT test with the best clinical evidence to support its use.”9
–Dr Douglas Rex, Past President of the American College of Gastroenterology (ACG)
The only FIT backed by proven clinical outcomes
Increase in patient compliance6
43.8%
Shown to improve up-to-date screening status
Reduction in annual CRC incidence6
25.5%
Reduction in cancer mortality6
52.4%
~90%
“Adherence to the screening program increased progressively over the years, reaching almost 90% of the target population.”10
FIT is more cost effective than other types of noninvasive colorectal screening tests11
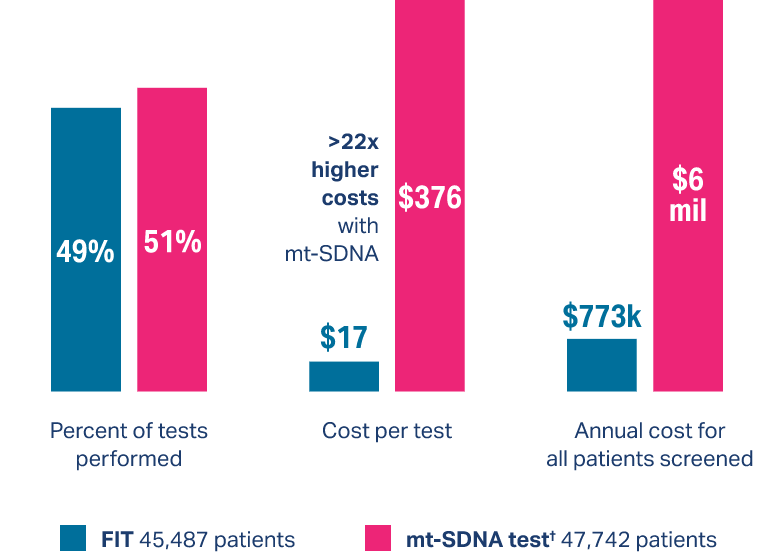
*Multi-target stool DNA test.
Improved patient experience and ease of use makes annual FIT screening a reality

At-home collection
99.8%
of patients returned the collection device correctly12

Single-sample
Only requires milligrams of sample from one bowel movement
90%
of survey respondents reported that the automated test collection device was simple-to-very easy to use12

No-mess process
93%
of respondents that had previously performed the Guaiac test collection preferred the FIT test collection procedure (which is completely closed and without dietary restrictions)12
Download the brochure
See how easy screening can be with OC-AUTO FIT


Meet your CRC screening goals with solutions and support to optimize your screening program
- In-service trainings, in person or remote
- Patient and provider educational materials
- Patient instructions in over 40 languages
- Business reviews to assess impact
- Mailing FIT directly to the patient’s home to help improve access to care
OC-Auto FIT
Excellent sensitivity and specificity get more of the right patients in for diagnostic procedures
| Specificity for colorectal cancer (true negative) | 94.9%13 |
| Sensitivity for colorectal cancer (true positive) | 73.8-84.513 |
| Ranking: USMSTF | Tier 13,5 |
OC-Auto Sensor io + Sensor Diana


Fully automated FIT analyzers designed with laboratories in mind

Increase productivity

Remove subjectivity of reading results

Update patient records automatically
| OC-Auto Sensor io | OC-Auto Sensor Diana | |
|---|---|---|
| Detection of fecal occult blood in stool for colorectal cancer screening |  |
 |
| Single samples with no dietary restrictions |  |
 |
| 15-day inoculated stability |  |
 |
| # of tests per hour | 88 | 280 |
| Closed sampling bottle |  |
 |
| Built-in sample bar code reader |  |
 |
| Latex agglutination immunoassay |  |
 |
| QC & calibration liquid ready |  |
- |
| Dimensions (width x depth x height) | 14.2” x 22.1” x 16.7” | 24.8” x 22” x 22” |

Ordering information
Contact us

Thank you for your submission. Someone will be in touch soon.
References:
- Siegel RL, Wagle NS, Cercek A, Smith, RA, Jemal A. Colorectal cancer statistics, 2023. CA Cancer J Clin. 2023;73(3):233-254. doi:10.3322/caac.21772
- Data & Progress. National Colorectal Cancer Roundtable. May 10, 2023. Accessed July 11, 2023. https://nccrt.org/data-progress/
- US Preventive Services Task Force, Davidson KW, Barry MJ, et al. Screening for colorectal cancer: US Preventive Services Task Force recommendation statement. JAMA. 2021;325(19):1965-1977. doi:10.1001/jama.2021.6238
- Shaukat A, Kahi CJ, Burke CA, Rabeneck L, Sauer BG, Rex DK. ACG Clinical Guidelines: Colorectal Cancer Screening 2021. Am J Gastroenterol. 2021;116(3):458-479. doi:10.14309/ajg.000000000000122
- Rex DK, Boland CR, Dominitz JA, et al. Colorectal Cancer Screening: Recommendations for Physicians and Patients from the U.S. Multi-Society Task Force on Colorectal Cancer. Am J Gastroenterol. 2017;112(7):1016-1030. doi:10.1038/ ajg.2017.174
- Levin TR, Corley DA, Jensen CD, et al. Effects of organized colorectal cancer screening on cancer incidence and mortality in a large community-based population. Gastroenterology. 2018;155(5):1383-1391. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2018.07.017
- Data on file with Polymedco, LLC.
- UPSTF. Public comment on draft recommendation statement and draft evidence review: screening for colorectal cancer. Accessed July 7, 2023 http://www.uspreventiveservicestaskforce.org/Announcements/News/Item/public-comment-on-draft-recommendation-statement-and-draftevidence-review-screening-for-colorectal-cancer
- NEJM Journal Watch: Summaries of and commentary on original medical and scientific articles from key medical journals. Published June 13, 2013. Accessed July 7, 2023 https://www.jwatch.org/na31297/2013/06/13/finding-best-fit-colorectalcancer-screening
- Roselló S, Simón S, Cervantes A. Programmed colorectal cancer screening decreases incidence and mortality. Transl Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019;4:84. doi:10.21037/tgh.2019.12.13.
- Allen CJ, Bloom N, Rothka M, et al. Comprehensive cost implications of commercially available noninvasive colorectal cancer screening modalities. J Am Coll Surg. 2023;10. doi:10.1097/XCS.0000000000000768
- Data on file internally with Polymedco, LLC. (2)
- Imperiale TF, Ransohoff DF, Itzkowitz SH, et al. Multitarget stool DNA testing for colorectal-cancer screening. N Engl J Med. 2014;370(14):1287-1297. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1311194
- Wolf AMD, Fontham ETH, Church TR, et al. Colorectal cancer screening for average-risk adults: 2018 guideline update from the American Cancer Society. CA Cancer J Clin. 2018;68(4):250-281. doi:10.3322/caac.21457